Gallbladder and Biliary Tree
- Cholelitiasis (Gallstones)
- Cholesterol stones
- Pure pigment (Bilirubin) stones
- Calcium bilirubinate stones
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder
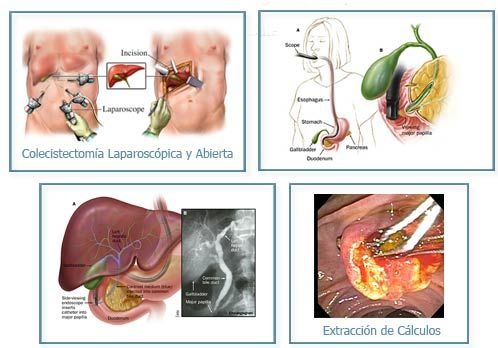
- Chronic cholecystitis: Diagnosis made by ultrasound to reveal stones. Treatment is laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
- Acute cholecystitis: Diagnosis by ultrasound, symptoms include, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, fever.
- Treatment is cholecystectomy. Complications such as emphysematous cholecystitis, gangrenous cholecystitis, perforated cholecystitis and biliary-enteric fistula.
- Acalculous cholecystitis: Also referred to as biliary dyskinesia. No stones are present. Treatment is cholecystectomy.
- Bile Duct Disorders
- Choledocholithiasis (Stones in common bile duct): Most stones are formed in the gallbladder and pass into the bile duct. Primary common duct stones can form in the absence of a gallbladder. Symptoms are right upper quadrant pain, jaundice, bilirubinuria. Treatment is done endoscopically by ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde CholangioPancreatography), in which stones are extracted by endoscopy. When stones are too large surgery is performed to explore the bile duct and extract stones.
- Cholangitis (Infection of the bile ducts): Infection of the bile duct caused by obstruction with pus in the duct. Patients present fever, abdominal pain and jaundice. Treatment includes antibiotics and relief of obstruction (ERCP or Surgery).
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Unknown etiology but develops progressive obstruction. Abdominal pain, jaundice. Diagnosed by ERCP and may be treated by placing stents endoscopically.
- Fibrosis of the Sphincter of Oddi: Is a disorder that causes right upper quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting. Treatment is by endoscopic sphincterotomy.
- Neoplasms
- Carcinoma of the Gallbladder: Most common complaint right upper quadrant pain. Treatment is cholecystectomy with wedge resection of the liver.
- Cholangiocarcinoma: Bile duct cancer, Klatskin´s tumor when the confluence of the hepatic duct is involved. Diagnosis by ERCP or MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography). Surgical treatment depends on stage of tumor.
- Choledochal cysts:Congenital malformations of the biliary tree. Majority are asymptomatic. Diagnosis by ultrasound, ERCP or MRCP. Treatment is surgery.
Stenosis and Injuries of the bile duct: These injuries or stenosis may be surgical, malignant or inflammatory. Treatment by ERCP or surgery.